Describe the Path of a Cardiac Impulse Through the Myocardium
Located in interarterial septum. _____ What divides the left and right side of the heart.

1 Anatomy And Histology Of The Cardiac Conduction System In The Download Scientific Diagram
This group of muscle cells is called the cardiac conduction system.

. Pacemaker Impulse Generation. Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical impulses through the heart. Purkinje Fibers Impulse Conduction.
Located in uppermost atrial wall. Trace the path of a nerve cardiac impulse through the. Then sends signal to A-V node send it down to A-V septem at the apex you need fibers.
The Purkinje fibers convey the action potential to the contractile cells of the ventricle. AV Node Impulse Conduction. Without stimulation from nerve fibers or any other outside agents the nodal cells initiate impulses that spread into the surrounding myocardium and stimulate cardiac muscle fibers to contract.
They extend throughout the myocardium from the apex of the heart toward the atrioventricular septum and the base of the heart. This causes both atria to contract. The SA node is located in the upper wall of the right atrium.
Describe the path of an electrical impulse through the hearts conduction system. Attracts impulse from brain sends signal to heart sinoatrial node absorbs i and amplephies it and throws it over the atria and contracts the aitria. In a normal healthy heart the electrical conduction pathway begins with the sinoatrial node receiving an electrical signal according to the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute.
Cardiac impulse then moves to the 3. The first time you hear the sound of a heart beat is the systolic pressure. What is the pacemakerWhat fibers cause a.
The first step of cardiac conduction is impulse generation. During this process the cardiac action potential reaches the AV Node located just above a small canal through the cardiac fibrous skeleton which connects the atria and the. The first step of cardiac conduction is impulse generation.
The sinoatrial SA node also referred to as the pacemaker of the heart contracts generating nerve impulses that travel throughout the heart wall. The Purkinje fibers are additional myocardial conductive fibers that spread the impulse to the myocardial contractile cells in the ventricles. Impulses travel throughout the atrial fibers via gap junctions in intercalated discs to the 2.
Compare the effect of ion movement on membrane potential of cardiac conductive and contractile cells. AV Bundle Impulse Conduction. The stethoscope is places at the brachial artery elbow and the cuff is wrapped around the arm the cuff is inflated and then the valve is released slowly.
Describe the epicardium myocardium and endocardium. Finally the signal reaches the bundle of His-Purkinje fibers. It is the pacemaker component.
Veins and arteries meet at _____ where nutrients are exchanged with body tissues. Serves as delay signal that allows for ventricular filling. Next the signal moves through the heart and reaches the atrioventricular node.
What are the 4 conduction pathways of the human heart. As the action potential travels through the conduction system and myocardium it will lead to atrial and ventricular depolarization and contraction. Describe the purpose of this electrical activity.
Describe the function of the sinoatrial node and trace the path of a nerve cardiac impulse through the cardiac conduction system. Begin at the lower interventricular septum to the apex of the heart then continue superiorly through the myocardium of the ventricles. 62 Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity.
The pacemaker cells do not have a. Describe cardiac output including factors involved in its regulation. Acts like a lighting rod.
Relate characteristics of an electrocardiogram ECG to events in the cardiac. Describe the function of the sinoatrial node and trace the path of a nerve impulse through the cardiac conduction system. The electrical impulse travels from the sinus node to the atrioventricular node also called AV node.
What is the apex of the heart and where is it located. The sequence of activation thus achieved is key in translating the lengthwise contraction of individual myocytes into the complex three-dimensional pumping motion of the heart. The rate at which the pacemaker cells fire is the heart rate.
Impulses originating in the sinoatrial node spread to the atria and via the specialized His-Purkinje conduction system to the ventricles. The 2 upper chambers of the heart atria are stimulated first and contract for a short period of time before the 2 lower chambers of the heart ventricles. Describe the size and location of the heart.
Explain the events associated with S1 and S2 heart sounds indicating where each of these sounds is best heard. Briefly describe the path of blood as it circulates through the heart blood enters heart from venae cavae and pulmonary veins heart inflated as blood enters atria and ventricles through A-V valves full atria contract topping off ventricles to full capacity A-V valves close ventricles contract forcing blood out of heart through semilunar valves.

Mechanisms Of Cardiac Arrhythmias From Automaticity To Re Entry Reentry Ecg Learning Cardiac Arrhythmia Cardiac Ventricular Tachycardia

Lecture 8 Heart Rhythmicity And Normal Ecg Flashcards Quizlet

Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And Physiology Ii

The Cardiac Conduction System Youtube
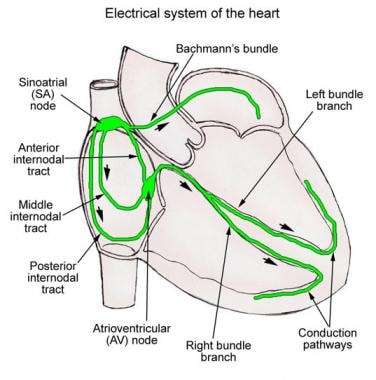
Conduction System Of The Heart Overview Gross Anatomy Natural Variants

The Conducting System Of Heart

Electrical Conduction System Of The Heart The Premier Ekg Resource For Medical Professionals Ekg Md Dr Anthony Kashou

Electrical Pathway Through The Heart Initiation Action Potential Timing Study Com
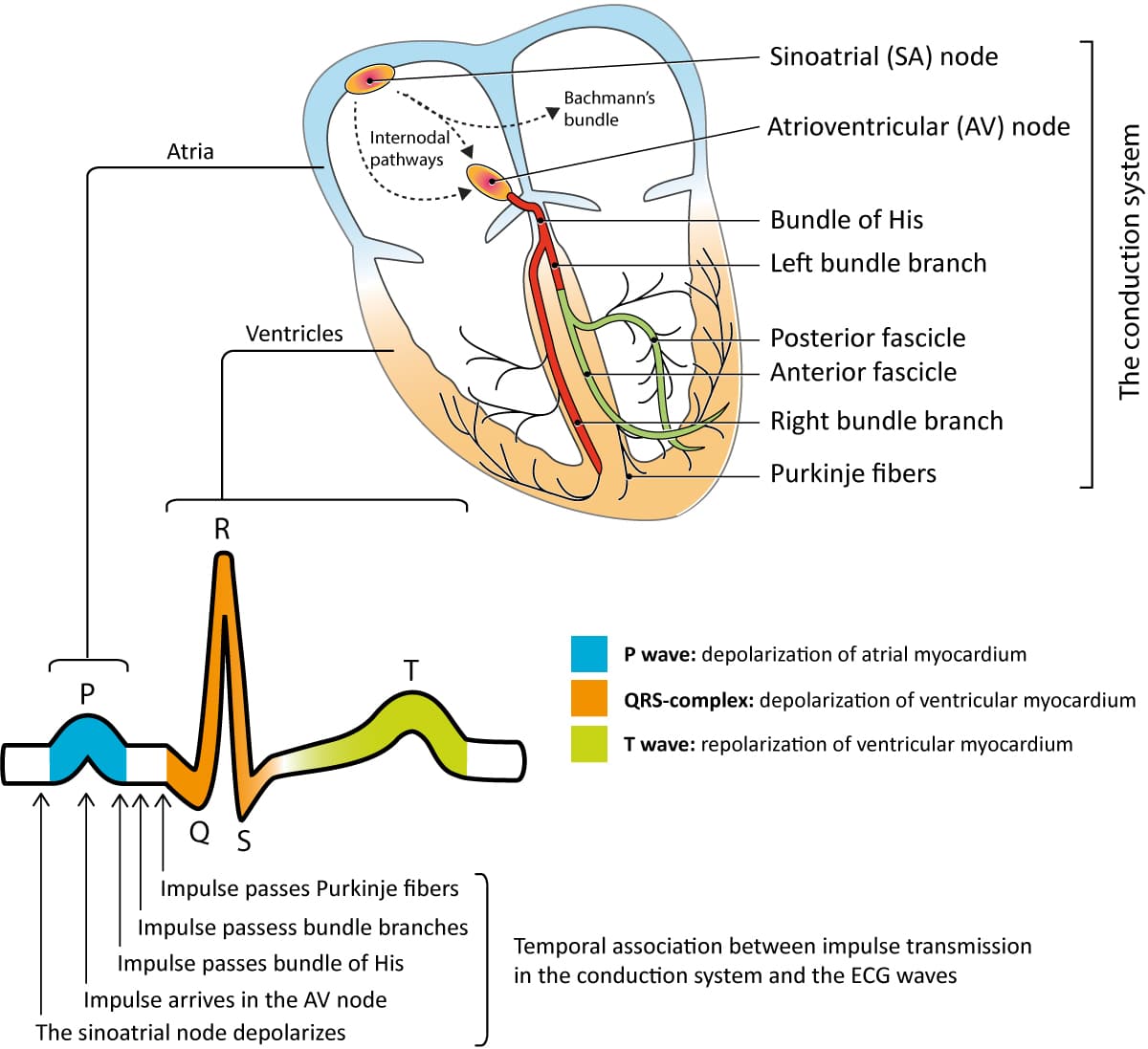
Clinical Electrocardiography And Ecg Interpretation Ecg Echo

Chapter 19 Cardiac Conduction System Flashcards Quizlet
Physiology Of Cardiac Conduction And Contractility Mcmaster Pathophysiology Review

Cardiac Conduction System Normal Function Of The Heart Cardiology Teaching Package Practice Learning Division Of Nursing The University Of Nottingham
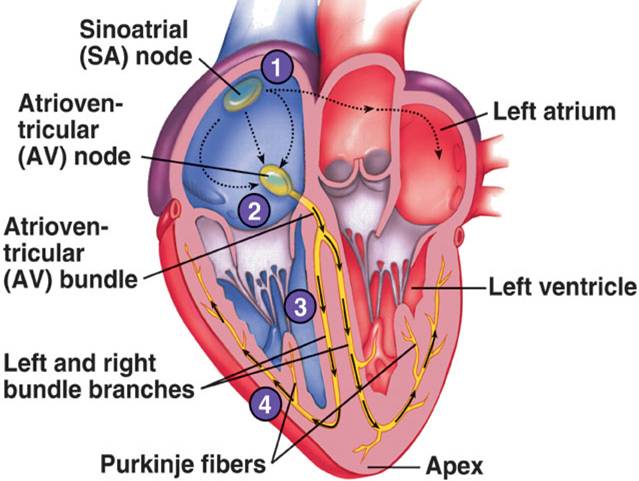
Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review


Comments
Post a Comment